Table of Contents
Introduction: Understanding the Digital Divide Between AR and VR

In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape as eality (AR) vs. Virtual Reality (VR), two groundbreaking technologies are consistently making headlines: Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). These immersive technologies are not just buzzwords; they are at the forefront of a digital revolution that promises to change how we interact with the world around us.
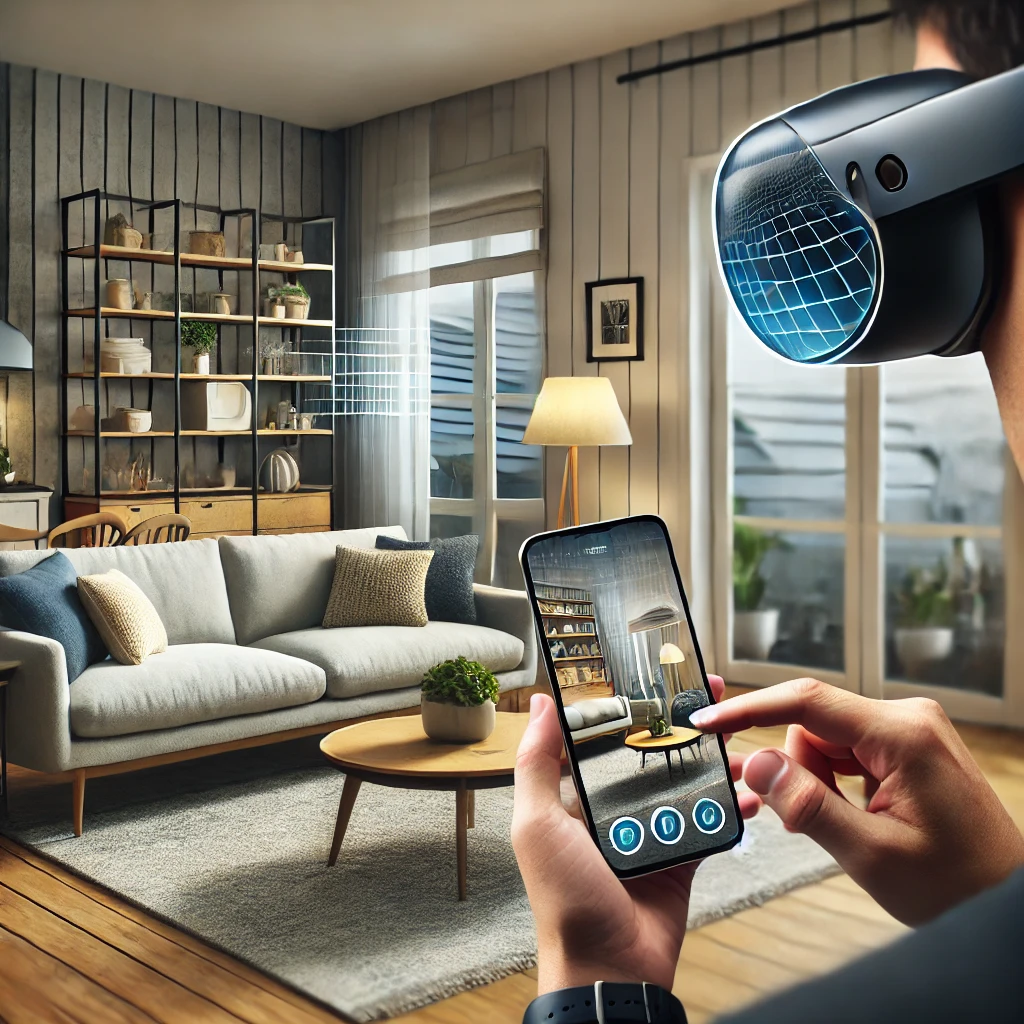
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the physical world, enhancing the user’s perception of their real environment. Through devices like smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses, AR projects information, graphics, and animations onto the world around us, providing a seamless blend of the digital and the real.
Virtual Reality (VR), on the other hand, immerses the user in a completely digital environment. By donning VR headsets, users are transported to entirely new worlds where they can interact with digital objects and environments as though they were real. This isolation from the physical world creates a fully immersive experience that is unmatched by any other technology.
As these technologies advance, American consumers are increasingly exposed to their transformative potential. But what exactly sets AR and VR apart, and what can we expect from their future development? Let’s explore.
Current Uses: Popular AR and VR Applications in the U.S.
AR and VR are no longer just futuristic concepts; they have already begun to integrate into various aspects of our daily lives. Here’s how American consumers are currently engaging with these technologies:
Augmented Reality (AR)
- Gaming: The phenomenal success of Pokémon GO demonstrated the power of AR in gaming. By allowing players to hunt for digital creatures in real-world locations, AR has made gaming more interactive and engaging. This blending of the physical and digital worlds has opened up new possibilities for gaming, with other titles like Harry Potter: Wizards Unite following suit.
- Retail: Imagine being able to visualize how a piece of furniture will look in your living room before you buy it. Retailers like IKEA and Amazon are already making this possible through AR apps that let consumers virtually place items in their homes. This technology not only enhances the shopping experience but also reduces the likelihood of returns.
- Education: AR is transforming classrooms by providing interactive learning experiences. For example, students can now explore 3D models of the human body or historical sites through AR apps, making education more engaging and effective. This interactive approach to learning helps students better understand complex subjects.
- Navigation: Google Maps has incorporated AR to make navigation more intuitive. Instead of relying solely on 2D maps, users can now see real-world environments with overlaid directions, points of interest, and information. This makes it easier to navigate unfamiliar areas, especially in complex urban settings.
Virtual Reality (VR)
- Gaming: VR has taken gaming to a whole new level. Platforms like Oculus Rift, PlayStation VR, and HTC Vive offer immersive experiences where players can step into virtual worlds. Unlike traditional gaming, VR allows users to interact with their surroundings in a 360-degree space, providing a sense of presence that is unparalleled.
- Entertainment: Beyond gaming, VR is also making waves in entertainment. Virtual tours, concerts, and movie experiences are becoming more common, giving users the feeling of being present in distant locations or events. This has particularly gained traction during the COVID-19 pandemic, where virtual events became a safe and viable alternative.
- Training and Simulation: VR is widely used for training purposes in industries like healthcare, aviation, and the military. By creating realistic simulations, VR allows professionals to practice in a safe environment, reducing the risks associated with real-world training. For example, surgeons can perform virtual surgeries before operating on actual patients, and pilots can simulate flights under various conditions.
- Social Interaction: Platforms like VRChat and AltspaceVR provide virtual spaces for socializing. Users can attend virtual events, meet new people, and even host gatherings, all within a digital environment. This aspect of VR is expected to grow as the technology improves, offering new ways to connect with others.
Market Trends: Growth and Consumer Adoption Rates
The AR and VR markets in the United States are experiencing rapid growth, driven by increased consumer interest and technological advancements.
Market Growth
According to industry reports, the AR market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 40% from 2021 to 2026. Similarly, the VR market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 35% during the same period. This growth is fueled by the expanding range of applications for these technologies, as well as increased investment from major tech companies.
Consumer Adoption
As AR and VR become more affordable and accessible, consumer adoption rates are rising. In the gaming sector, VR has already gained significant traction, particularly among enthusiasts seeking immersive experiences. Meanwhile, AR’s broader range of applications, from retail to education, has led to its adoption in more diverse sectors.
Investment
Tech giants like Apple, Google, Facebook (Meta), and Microsoft are investing heavily in AR and VR. These companies are not only developing new hardware and software but also acquiring startups that specialize in these technologies. This influx of investment is likely to drive further innovation and growth in the AR and VR markets.
Future Innovations: Upcoming AR and VR Technologies
The future of AR and VR is bright, with numerous innovations on the horizon that promise to make these technologies even more integral to our lives.
Augmented Reality (AR)
- AR Glasses: One of the most anticipated developments in AR is the introduction of advanced AR glasses. Companies like Apple and Facebook are rumored to be working on devices that could potentially replace smartphones for many functions. These glasses would overlay digital information directly onto the user’s field of vision, allowing for seamless integration of digital content into everyday life.
- Enhanced Interactivity: Future AR systems will likely feature more interactive and intuitive controls. Gestures, eye-tracking, and voice commands will play a significant role in how users interact with digital content. For example, users might be able to manipulate virtual objects with hand movements or navigate through apps using eye movements.
- Spatial Computing: As AR evolves, it will become more adept at understanding and interacting with the physical environment. This could lead to more complex applications in areas like home automation, where AR could provide real-time information about household systems, or in industrial maintenance, where AR could offer step-by-step guides for repairs.
Virtual Reality (VR)
- Improved Hardware: The next generation of VR headsets is expected to feature higher resolution displays, wider fields of view, and lighter, more comfortable designs. These improvements will enhance the overall user experience, making VR more appealing to a broader audience.
- Haptic Feedback: One of the most exciting areas of VR development is haptic feedback, which aims to provide realistic tactile sensations in virtual environments. Advanced haptic systems could make virtual interactions feel almost indistinguishable from real-life experiences, significantly increasing the immersion factor.
- Social and Collaborative VR: As VR technology improves, there will be a greater focus on social and collaborative applications. This includes virtual workspaces where colleagues can collaborate in real-time, virtual classrooms for remote education, and social platforms where users can interact in a shared virtual space.
Challenges: Technical and User Experience Hurdles
Despite the promising future of AR and VR, several challenges remain that could hinder widespread adoption.
Technical Challenges
- Hardware Limitations: While AR and VR devices have come a long way, they still face limitations. Current hardware can be bulky, and high-quality devices are often expensive, making them less accessible to the average consumer. Additionally, AR glasses that are both stylish and functional remain elusive.
- Battery Life: The battery life of AR and VR devices is another significant hurdle. Prolonged use often drains batteries quickly, which can be frustrating for users, especially in scenarios where continuous use is required, such as gaming or professional applications.
- Connectivity: For AR and VR to provide seamless experiences, high-speed, low-latency internet connections are essential. However, such connectivity is not yet universally available, particularly in rural areas. This limits the reach of these technologies and could slow down their adoption.
User Experience Challenges
- Motion Sickness: A common issue with VR is motion sickness, which affects a significant portion of users. This can be a major barrier to prolonged use, as it causes discomfort and discourages users from fully engaging with the technology.
- Privacy Concerns: AR, in particular, raises privacy concerns because it often requires access to cameras and location data. As AR becomes more integrated into everyday life, concerns about how this data is collected, stored, and used will need to be addressed.
- Content Availability: The success of AR and VR hinges on the availability of compelling content. While the range of applications is growing, there is still a need for more high-quality content that can attract and retain users across different sectors.
Conclusion: The Future of AR and VR for American Consumers
The future of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality is brimming with potential, promising to reshape how American consumers interact with both digital and physical worlds. As AR and VR technologies continue to evolve, they will offer increasingly immersive and interactive experiences, transcending the realms of gaming and entertainment to impact education, professional training, social interaction, and beyond.
While technical and user experience challenges remain, the ongoing investment and innovation by tech giants are likely to overcome these hurdles, paving the way for AR and VR to become integral parts of everyday life in the U.S. As these technologies mature, the boundaries between the digital and physical worlds will continue to blur, creating new opportunities for engagement, learning, and entertainment.